[Spark] Learning Spark(1) - Spark Jobs, Stages, Tasks
Learning Spark(1) - Spark Jobs, Stages, Tasks
- Spark Jobs
- Spark Stages
- Spark Tasks
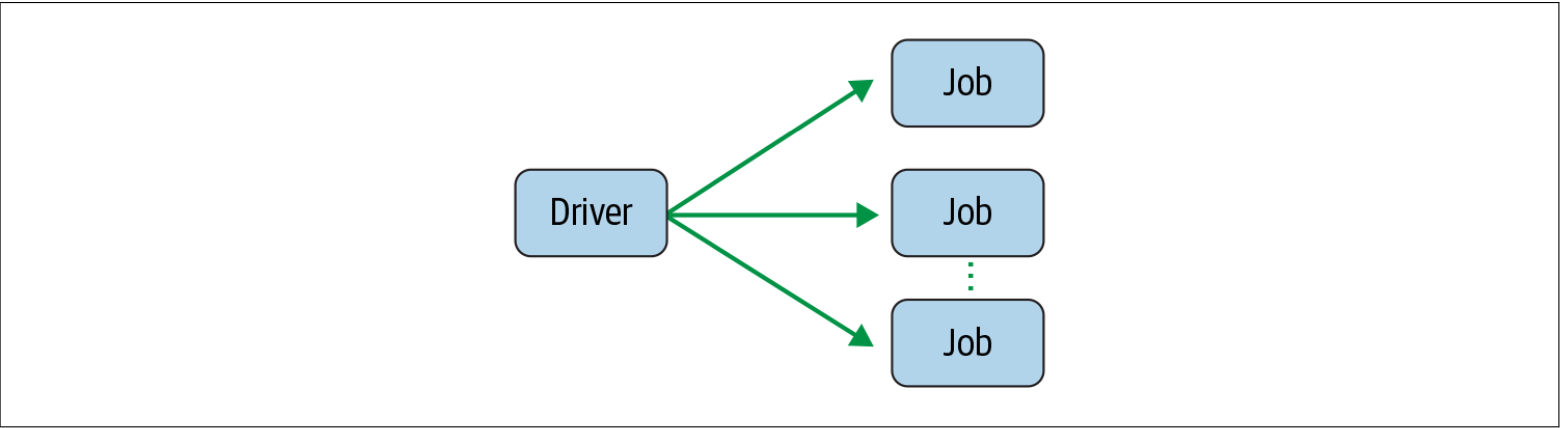
Spark Jobs
- During interactive sessions with Spark shells, the driver converts your Spark application into one or more Spark jobs.
- It then transforms each job into a DAG.
- This, in essence, is Spark’s execution plan, where each node within a DAG could be a single or multiple Spark stages.
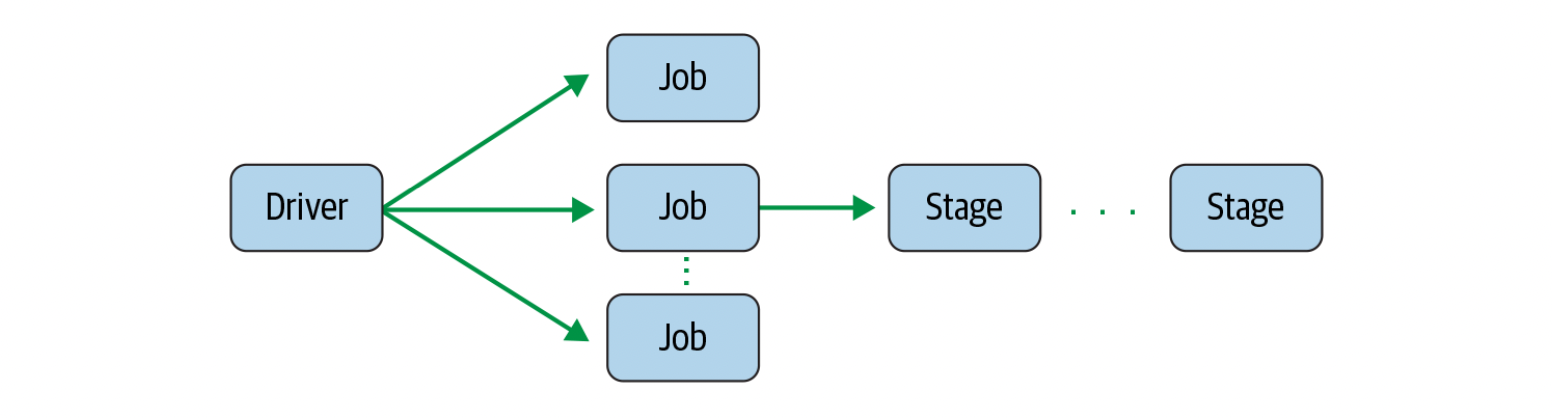
Spark Stages
- As part of the DAG nodes, stages are created based on what operations can be per‐ formed serially or in parallel
- Not all Spark operations can happen in a single stage, so they may be divided into multiple stages.
- Often stages are delineated on the operator’s computation boundaries, where they dictate data transfer among Spark executors.
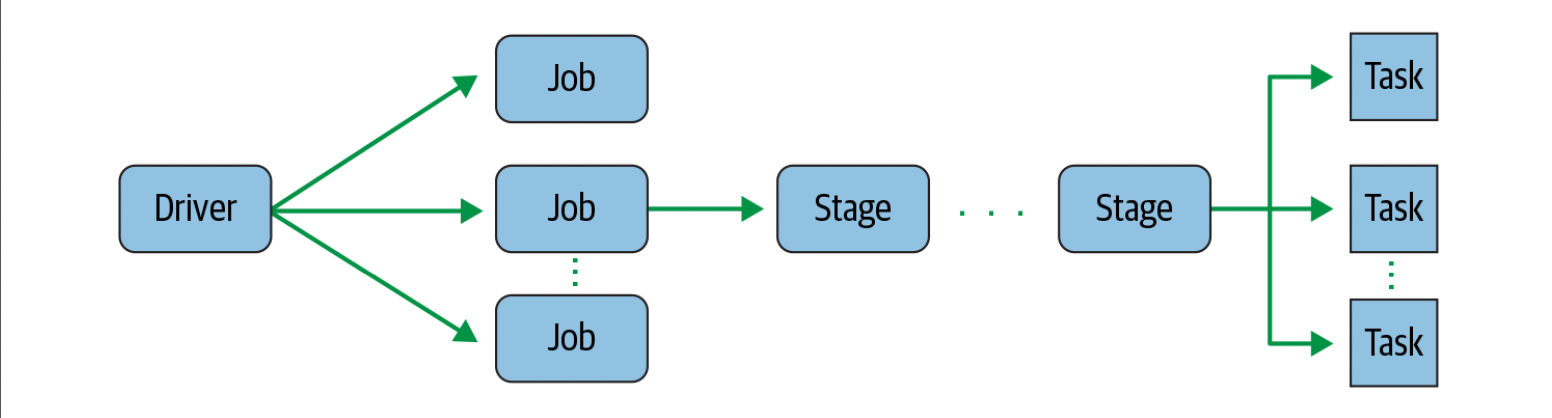
Spark Tasks
- Each stage is comprised of Spark tasks (a unit of execution), which are then federated across each Spark executor; each task maps to a single core and works on a single partition of data.
- As such, an executor with 16 cores can have 16 or more tasks working on 16 or more partitions in parallel, making the execution of Spark’s tasks exceedingly parallel.
ref
- Learning Spark, 2nd Edition, by Jules S. Damji, Brooke Wenig, Tathagata Das, and Denny Lee. Copyright 2020 Databricks, Inc., 978-1-492-05004-9.
